Phonetics is the study of how we produce and hear sounds in speech. Imagine trying to learn a new language without knowing the sounds that make up words. It’d be a challenge, right? That’s why phonetics is crucial. It’s like the ABCs of spoken language.

Phonetics plays a massive role in helping us communicate effectively. When you understand the sounds, it’s easier to pronounce words correctly, avoid misunderstandings, and even pick up new languages faster. Whether you’re a language nerd or just someone looking to improve their English, getting a handle on phonetics is a game-changer.
You can’t talk about phonetics without mentioning the International Phonetic Alphabet, or IPA. This is a special system where each sound gets its own unique symbol. Think of it as the Rosetta Stone for speech sounds. With the IPA, you can read the pronunciation of any word in any language and know exactly how it should sound. It’s pretty handy!
English sounds are split into two main categories: consonants and vowels. Consonants involve some level of blockage of airflow in the mouth, like ‘t’ or ‘m’. Vowels, on the other hand, are made with a relatively open vocal tract and include sounds like ‘a’ and ‘e’. Knowing the difference is key to understanding how words are formed and how they should sound.
Vowel Sounds: Exploring the Heart of English Pronunciation
Vowel sounds are truly the heartbeat of spoken English. These are the sounds you make with your mouth open and your air flowing unobstructed. There’s a fascinating array of vowel sounds in English, split into short vowels, long vowels, and diphthongs (which are like vowel sound hybrids).
Short vowels are quick and snappy: think of the ‘a’ in ‘cat’ or the ‘e’ in ‘bed’. Long vowels stretch out more, like the ‘i’ in ‘kite’ or the ‘o’ in ‘nose’. Diphthongs mix two vowel sounds together in one syllable, such as the ‘oi’ in ‘coin’ or the ‘ou’ in ‘loud’. Mastering these can be tricky, but once you nail them, your pronunciation improves significantly.
Differentiating between these vowel sounds can feel like a tongue twister at times. Start by focusing on the position of your tongue and lips. For example, notice how your tongue is high in your mouth for the long ‘ee’ sound, like in ‘see,’ versus lower for the short ‘e’ in ‘bed’. Being mindful of these positions can really help.
Everyone struggles with vowel sounds at some point, especially if English isn’t your first language. The key is consistency. Practice regularly and pay attention to subtle differences in sound. If you mix up ‘ship’ and ‘sheep,’ don’t sweat it—just keep practicing. Listen to native speakers, mimic their pronunciation, and use tools like the IPA to guide you.
One of the best ways to improve your vowel pronunciation is through exercises. Try minimal pair drills, where you practice with pairs of words that only differ by one vowel sound, such as ‘bit’ and ‘beat’. Recording yourself and playing it back can also reveal areas for improvement. Apps and online resources can offer additional practice tools and feedback to help you along the way.
Consonant Sounds: The Building Blocks of Clear English Speech
Consonants are like the bricks and mortar of spoken English. These are the sounds where your speech organs come together, creating various levels of airflow blockage. Whether you’re saying ‘t’ or ‘m’, consonants structure your speech and make words distinct.

A big thing with consonants is understanding the difference between voiced and voiceless sounds. Voiced sounds, like ‘b’ and ‘d’, use your vocal cords. If you put your hand on your throat while saying them, you’ll feel a vibration. Voiceless sounds, like ‘p’ and ‘t’, don’t use your vocal cords, so there’s no vibration.
Another important aspect is consonant clusters. These are groups of consonants together in a word without a vowel in between, like ‘str’ in ‘street’ or ‘mp’ in ‘jump’. They can be tough to master, especially if your native language doesn’t have similar clusters.
Aspiration in consonant sounds adds another layer of complexity. It’s the puff of air you might hear or feel after certain consonants, like the ‘p’ in ‘pat’ versus the ‘sp’ in ‘spat’. Mastering this can make your English sound more natural and fluent.
To get better at consonants, repetitive practice is key. Use tools like tongue twisters to enhance your fluency. For example, try saying ‘She sells sea shells by the sea shore’ quickly without stumbling. It’s harder than it seems and great practice. Recording your speech and comparing it with native speakers can offer invaluable feedback too.
Connecting It All: Improving Overall Pronunciation and Fluency
Getting the hang of individual sounds is only part of the battle. To sound fluent, understanding stress, rhythm, and intonation is crucial. Stress dictates which parts of words and sentences get emphasis, turning ‘record’ from a noun to a verb depending on whether you stress the first or second syllable.
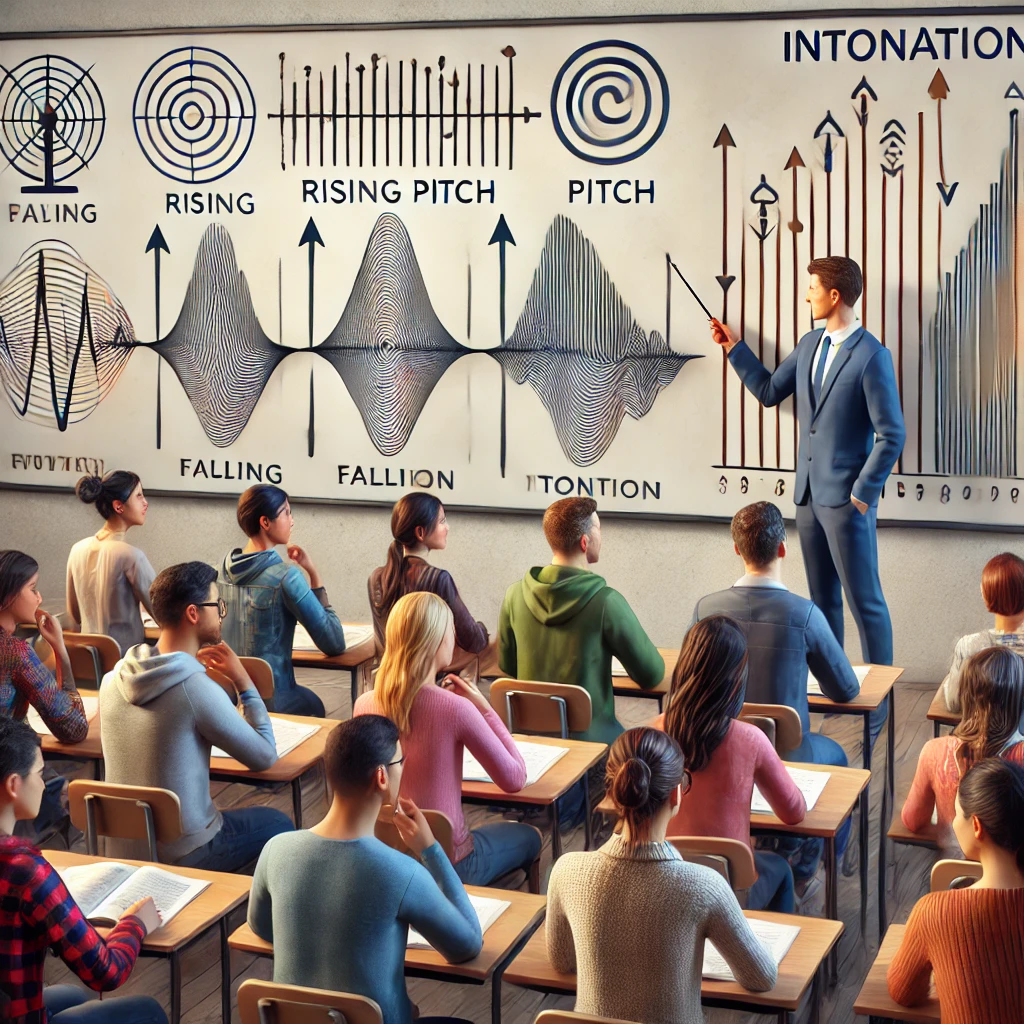

Rhythm ties in closely with stress, giving English its characteristic flow. Listen to native speakers and you’ll notice a pattern. Mimicking these speech patterns can make your English much more natural-sounding.
Intonation, or the rise and fall of pitch in speech, conveys meaning and emotion. Just changing your intonation can turn a statement into a question or express sarcasm. Practicing this can help you sound more engaging and expressive, not monotone.
Linking sounds together, known as connected speech, can also make a big difference. Native speakers often blend words together, making ‘want to’ sound like ‘wanna’. Understanding and practicing these transitions can boost your listening and speaking skills.
Mispronunciations happen to everyone, but recognizing common errors is the first step to fixing them. If you often mix up ‘th’ sounds, for example, focus on practicing words like ‘think’ and ‘this’. Consistent practice here sharpens your accuracy.
Continuous improvement requires the right tools and resources. Use language learning apps, watch videos, and engage in conversations with native speakers. Websites with pronunciation guides and online classes can also be very helpful. The key is to keep practicing and exposing yourself to English as much as possible.
Leave comments and questions in the comments section below.

Hi Kbob,
This article provides an insightful exploration of phonetics and its crucial role in mastering English pronunciation. By breaking down the nuances of vowel and consonant sounds and introducing the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), it equips readers with essential tools for improving their speaking skills.
The practical tips on stress, rhythm, and intonation further enhance its value, offering effective strategies for achieving greater fluency. Additionally, the emphasis on regular practice and the use of tools like minimal pairs and tongue twisters makes it a comprehensive resource for anyone eager to refine their pronunciation and communicate more effectively in English.
Cheers
John
Hi John, thanks for your comments. Leave them anytime. I will promptly reply.
KBob